H-1B Fee Policy Analysis: Strategic Implications
One week ago, on September 21, 2025, the President of the United State (Donald J. Trump) implemented an immediate $100,000 fee on all new H-1B visa petitions—a policy designed to encourage greater investment in American workforce development. This unprecedented cost increase fundamentally alters the economics of international talent acquisition across technology, consulting, finance, and retail sectors while creating new incentives for domestic talent cultivation.
Market Impact
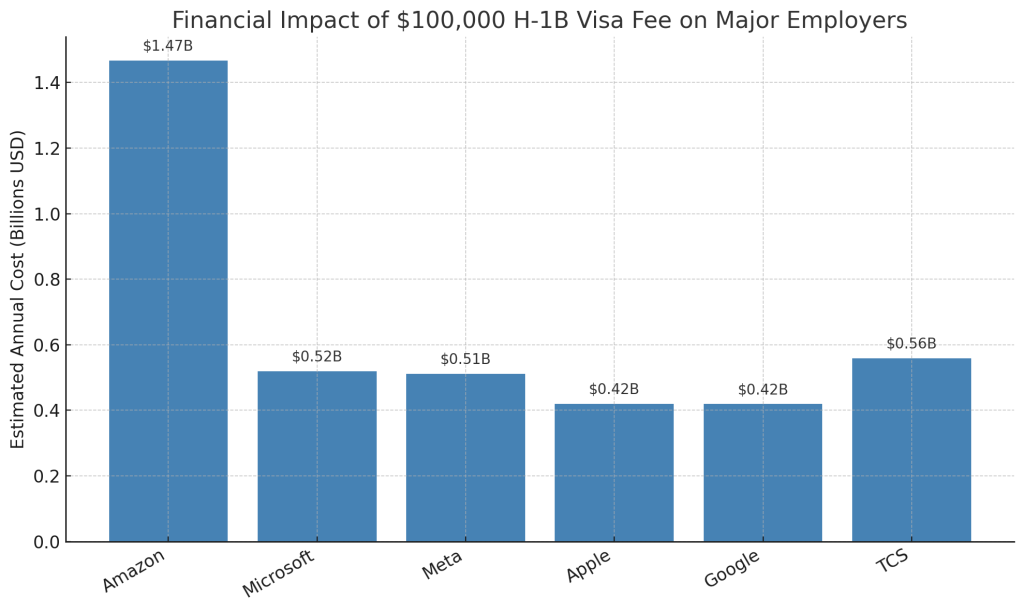
Massive Cost Exposure: The financial implications are staggering across major H-1B sponsors:
- Amazon: 14,667 petitions = $1.46 billion exposure
- TCS: ~5,590 petitions = $559M exposure
- Microsoft: ~5,190 petitions = $519M exposure
- Meta: ~5,120 petitions = $512M exposure
- Apple: ~4,200 petitions = $420M exposure
- Google: ~4,190 petitions = $419M exposure
These figures represent fundamental shifts in talent acquisition economics, with some companies facing costs equivalent to entire division budgets.
Competitive Rebalancing: The policy creates stark winners and losers based on H-1B dependency. Companies with historically lower visa utilization gain immediate cost advantages, while H-1B-dependent firms face margin compression. However, critics argue this disproportionately disadvantages smaller tech firms and startups that cannot absorb the high costs, potentially creating unfair advantages for well-funded corporations that can weather the financial impact.
Operational Transformation: Organizations will likely accelerate three strategic pivots: expanded offshore delivery models, aggressive automation adoption, and enhanced nearshore partnerships in Mexico and Canada. While reducing immediate costs, these shifts may compromise client proximity, cultural alignment, and innovation velocity—creating long-term competitive risks despite short-term savings. Critics warn this could force high-value work overseas, undermining the policy’s domestic employment objectives.
Domestic Talent Premium: The policy’s intended effect—driving investment in American workers—will likely materialize through expanded training programs, university partnerships, and apprenticeship initiatives. However, immediate talent scarcity may inflate wages for specialized roles, creating additional cost pressures even as companies pivot toward domestic hiring. Opposition groups argue this approach may backfire by discouraging top global talent essential for U.S. innovation leadership, particularly in competitive fields like artificial intelligence.
Healthcare System Impact: Medical organizations, including the American Medical Association, warn the fee will exacerbate physician shortages, especially in rural and underserved areas. With foreign-born physicians comprising nearly 25% of the U.S. medical workforce and filling critical roles in primary care, psychiatry, and pediatrics, the policy could have far-reaching public health consequences beyond its intended economic effects.
Legal & Regulatory Landscape
Constitutional Challenges: Legal challenges appear inevitable, with multiple avenues of attack. Immigration advocacy groups, including the American Immigration Council, assert the executive branch lacks authority to impose a $100,000 fee, as Congressional authorization is limited to cost-recovery charges for processing applications. Additional challenges may include:
- Due process violations due to lack of proper rulemaking procedures
- Arbitrary and capricious fee determination under administrative law
- Equal protection arguments regarding disproportionate industry impact
Legal Precedent Questions: Unlike Trump v. Hawaii (2018), which upheld presidential immigration authority on national security grounds, this policy’s economic justification may not receive the same judicial deference. Legal experts note the distinction could prove significant in court challenges.
Policy Durability: The unilateral imposition of fees at this magnitude lacks historical precedent, creating uncertainty around enforcement consistency and judicial review outcomes. Industry coalitions are mobilizing for legislative intervention, regulatory modification, or court-ordered relief.
Strategic Response Framework
Immediate Actions:
- Exposure Quantification: Calculate precise cost impact by business unit, skill category, and geographic region
- Budget Reallocation: Shift capital from visa fees toward domestic talent development programs
- Vendor Assessment: Evaluate suppliers’ H-1B dependency to anticipate service cost increases
Medium-Term Adaptations: 4. Workforce Architecture: Redesign delivery models with higher offshore ratios while maintaining quality standards 5. Talent Pipeline Investment: Establish partnerships with American universities, coding bootcamps, and technical schools 6. Policy Engagement: Join industry coalitions pursuing legislative relief or regulatory modifications
Long-Term Positioning: 7. Innovation Resilience: Develop strategies to maintain R&D velocity despite potential talent constraints 8. Scenario Planning: Model business performance under various policy evolution scenarios 9. Market Positioning: Communicate workforce development commitments to stakeholders while managing client expectations around delivery model changes
Outlook
This policy represents more than a cost increase—it’s a strategic inflection point requiring fundamental reconsideration of talent strategies. The administration frames the fee as necessary to prioritize American workers and reduce H-1B program abuse, while opponents argue it will damage U.S. competitiveness and innovation capacity without creating significant new domestic employment.
Economic analysis suggests the policy may achieve unintended consequences: rather than boosting American jobs, it could accelerate offshoring and automation while harming sectors like healthcare that depend on specialized foreign talent. Think tanks note that major Indian IT firms already employ substantial American workforces, meaning the fee increases costs without necessarily creating new positions.
Companies that successfully balance domestic workforce investment with operational efficiency—while navigating potential legal challenges and policy modifications—will emerge stronger. Those unable to adapt face sustained competitive disadvantage. The ultimate measure of success will be maintaining innovation capacity and client satisfaction while managing this complex new economic and regulatory reality.
The policy’s durability remains uncertain given strong legal challenges and industry opposition, requiring scenario planning across multiple potential outcomes.
Bottom Line: The $100,000 H-1B visa fee is now live, introducing unprecedented labor costs designed to incentivize greater investment in American talent development. While this policy shift aims to prioritize domestic workforce opportunities, it faces substantial legal challenges and threatens to reshape multiple industries in unintended ways. Large firms may weather the storm through increased training budgets and domestic recruiting, but mid-tier companies and critical sectors like healthcare face disproportionate pressure.
The higher barriers to H-1B utilization will likely accelerate offshore reliance and automation adoption, potentially undermining the policy’s intended domestic benefits while exacerbating physician shortages in underserved areas. Companies must now weigh substantial international talent costs against expanded investments in American worker development, while preparing for potential legal reversals or policy modifications.
This represents a strategic inflection point complicated by regulatory uncertainty: organizations that can successfully pivot toward robust domestic talent cultivation—while maintaining contingency plans for various legal and policy outcomes—will gain competitive advantage. Swift adaptation through enhanced domestic workforce strategies, coordinated legal advocacy, and scenario planning across multiple potential futures will be critical for maintaining both talent quality and operational viability.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.